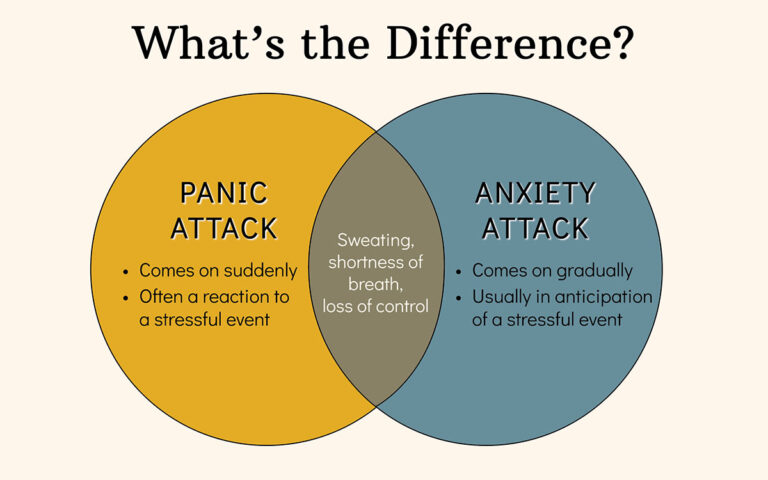
Panic attacks and anxiety attacks are terms often used interchangeably, but they represent different experiences with distinct symptoms and triggers. Understanding the differences between the two can help in identifying and managing these conditions more effectively. This article explores the key differences between panic attacks and anxiety attacks, including their symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
What is a Panic Attack?
A panic attack is an intense episode of fear or discomfort that typically peaks within minutes and is often accompanied by physical symptoms. These attacks can occur unexpectedly and without an obvious trigger, making them particularly distressing.
- Symptoms of a Panic Attack: Panic attacks are characterized by sudden and overwhelming fear or discomfort. Common symptoms include:
- Rapid heartbeat (palpitations)
- Shortness of breath or hyperventilation
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Trembling or shaking
- Sweating
- Nausea or stomach pain
- Feeling of choking
- Fear of losing control or “going crazy”
- Fear of dying
- Causes of Panic Attacks: The exact cause of panic attacks is not well understood, but they are believed to be linked to a combination of genetic, biological, and environmental factors. Stress, trauma, or significant life changes can also trigger panic attacks.
What is an Anxiety Attack?
An anxiety attack, on the other hand, is a more gradual build-up of anxiety, often related to a specific stressor or situation. Anxiety attacks are typically less intense than panic attacks, but they can last longer and cause significant distress.
- Symptoms of an Anxiety Attack: The symptoms of an anxiety attack are generally related to excessive worry or fear. Common symptoms include:
- Restlessness or feeling on edge
- Irritability
- Fatigue
- Difficulty concentrating
- Muscle tension
- Sleep disturbances
- Excessive worry about specific situations or events
- Nausea or gastrointestinal issues
- Causes of Anxiety Attacks: Anxiety attacks are usually triggered by stressors such as work, relationships, health concerns, or financial issues. They are often associated with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) but can occur in anyone facing overwhelming stress.
How Do Panic Attacks Differ from Anxiety Attacks?
Understanding the differences between panic attacks and anxietyattacks is crucial for proper identification and treatment.
- Onset and Duration: Panic attacks have a sudden onset, often occurring without warning, and typically peak within 10 minutes before subsiding. Anxiety attacks, however, have a more gradual onset and can last for hours or even days.
- Intensity of Symptoms: Panic attacks are usually more intense, with physical symptoms that can mimic those of a heart attack. Anxiety attacks are generally less intense but can still cause significant discomfort and distress.
- Triggers: Panic attacks can occur without an obvious trigger, while anxietyattacks are usually linked to specific stressors or worries.
- Mental vs. Physical Focus: Panicattacks often involve intense physical symptoms, while anxiety attacks are more focused on mental symptoms like worry and fear.
Can You Have Both Panic and Anxiety Attacks?
It is possible to experience both panic attacks and anxietyattacks, either separately or together. For example, someone with generalized anxiety disorder may experience frequent anxiety attacks and occasionally suffer from panicattacks during periods of extreme stress.
- Overlap in Symptoms: While panic and anxiety attacks are distinct, they share some overlapping symptoms, such as a racing heart, shortness of breath, and a sense of impending doom. This overlap can sometimes make it difficult to distinguish between the two.
- Impact on Daily Life: Both panic and anxiety attacks can significantly impact daily life, affecting work, relationships, and overall well-being. It’s important to seek professional help if these attacks become frequent or disruptive.
How to Manage and Treat Panic Attacks
Managing panic attacks involves a combination of self-care strategies and professional treatment. Here are some effective methods:
- Breathing Exercises: Controlled breathing can help reduce the intensity of a panic attack. Techniques such as deep breathing or box breathing can be particularly effective.
- Mindfulness and Grounding Techniques: Focusing on the present moment can help you regain control during a panic attack. Grounding techniques, such as focusing on physical sensations or repeating a calming phrase, can be helpful.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a common treatment for panic disorder, helping individuals identify and change negative thought patterns that contribute to panic attacks.
- Medications: In some cases, medications such as antidepressants or benzodiazepines may be prescribed to help manage panic attacks. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan.
How to Manage and Treat Anxiety Attacks
Managing anxiety attacks involves identifying triggers and using coping strategies to reduce anxiety. Here are some tips:
- Identify Triggers: Keeping a journal to track your anxiety and identify triggers can help you understand what causes your anxiety attacks and how to avoid or manage them.
- Relaxation Techniques: Techniques such as progressive muscle relaxation, meditation, and yoga can help reduce overall anxiety and prevent anxiety attacks.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep can significantly reduce anxiety levels and prevent anxiety attacks.
- Therapy: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is also effective for treating anxiety attacks, helping individuals change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- Medications: For those with severe anxiety, medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or benzodiazepines may be prescribed. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any medication.
When Should You Seek Help?
Both panic attacks and anxiety attacks can be overwhelming, but professional help is available. It’s important to seek help if:
- Frequent Attacks: You experience frequent panic or anxietyattacks that interfere with your daily life.
- Avoidance Behaviors: You start avoiding situations or places due to fear of having an attack.
- Physical Health Concerns: The physical symptoms of your attacks are severe, and you’re worried about your health.
- Impact on Mental Health: Your mental health is suffering, and you feel unable to cope with your anxiety or panic.
Conclusion:
Panic attacks and anxiety attacks are both challenging experiences, but understanding the differences between the two can help in managing them more effectively. While panic attacks are characterized by sudden, intense physical symptoms, anxiety attacks involve a more gradual build-up of worry and fear. Both conditions can significantly impact your quality of life, but with the right strategies and professional support, they can be managed successfully.
If you or someone you know is struggling with panic or anxiety attacks, reaching out to a mental health professional is a crucial step toward recovery. With the right treatment and coping strategies, it is possible to regain control and live a fulfilling life.